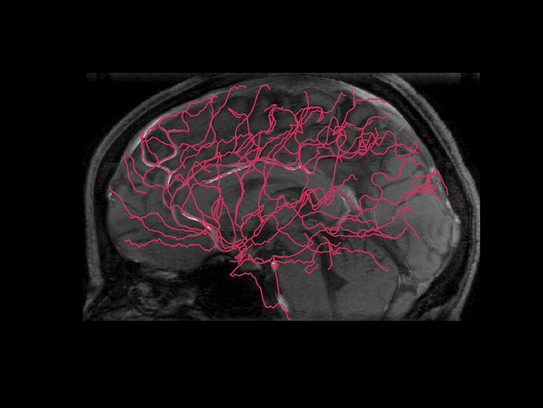
Circulating blood as an organ at risk: a dynamic framework for dose calculation during advanced radiation therapy
The latter part of Research Project 1.3 requires spatiotemporal simulations involving the dynamics of the beam delivery and anatomical motion. Research Project 1.4: Circulating blood as an organ at risk: a dynamic framework for dose calculation during advanced radiation therapy will implement even more elaborated patient models in the time domain, which are particularly relevant for studying dose-rate effects in patients.
This project investigates how radiation therapy affects circulating lymphocytes—highly radiosensitive immune cells that have long been overlooked as an organ-at-risk. A key innovation is the optimization of treatment plans in the time domain, accounting for the continuous movement of blood and the dynamic nature of radiation delivery. We will study how the timing and spatial distribution of dose rates influence lymphocyte exposure across different treatment modalities, including conventional photon therapy, proton arc therapy, and shoot-through FLASH proton therapy. The latter also enables simultaneous proton radiography, creating a direct link to Research Project 1.1.